
Share This Post
If your skin is regularly exposed to ultraviolet (UV) rays outdoors or in a tanning bed, it will be seriously damaged. Sun damage causes lots of changes to our skin, not only aesthetic problems but even more serious conditions like skin cancer.
We are constantly exposed to UV radiation. Even artificial lights, including computer and TV screens, or energy-saving bulbs cause damage to the skin. But most of the UV rays come from the sun.
The ultraviolet radiation spectrum is divided into three regions called UVA, UVB and UVC.
UVA rays are the most harmful for us. They can penetrate the clouds, the air, and deep into the skin, all the way into the inner layers getting straight into the dermis.
We don’t feel them, but once they reached the dermis, they can destroy cells essential to healthy skin, increase your chances for photoaging and skin cancer. UVA rays also destroy vitamin D, produced by UVB rays.
UVB rays only penetrate the top layer of the skin, the epidermis, causing direct physical damage by sunburn, and another major cause of skin cancer.
At the same time, exposure of the human epidermis to sunlight produces melanin, moderately tanning the skin by increasing the amount of photoprotective pigment. In this way, melanin prevents the skin from the potentially damaging effects of UV light.
UVB rays are also essential in the manufacturing of vitamin D. However, they are not able to penetrate the clouds, hence we cannot produce vitamin D in winter.
For humans, it takes about 20 minutes to convert pre-vitamin D to active vitamin D. Darker-skinned people need 5 times longer time to produce vitamin D than pale-skinned people because the melanin in the epidermis prevents UVB rays from penetrating.
Both UVA and UVB rays destroy vitamin A in the epidermis and the Langerhans cells at the skin barrier, the latter being responsible for the immunity of the skin.
Are you aware that using solariums involve serious health risks? Bulbs in sunbeds emit three times more intense UVA than natural sun rays, and even the UVB intensity may approach that of bright sunlight.
UVC rays are the strongest but have the shortest wavelengths, not long enough to reach our skin, actually, they are mostly absorbed by the atmospheric ozone at the stratosphere. Thus, the only way we can be exposed to UVC radiation is from an artificial light like a lamp or laser.

The importance of daily sun protection from UV rays should not be underestimated. Our skin should not be exposed to direct sunlight for long hours.
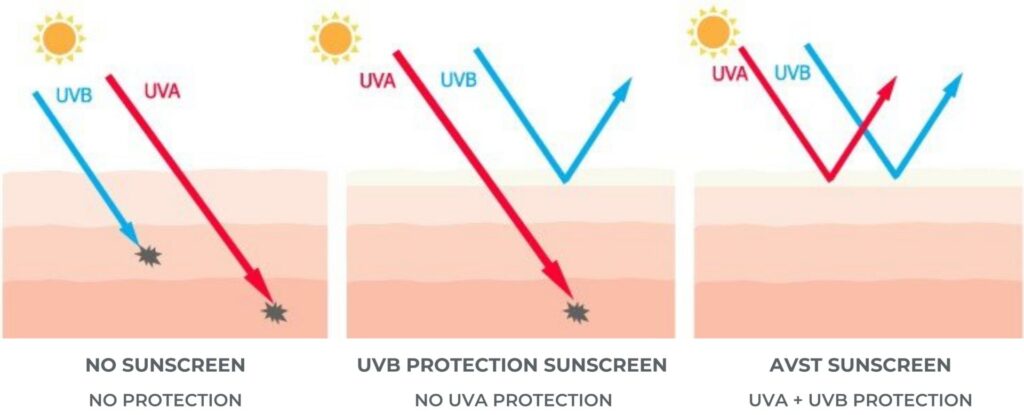
Sunbathing, therefore, is not recommended at all, even if you use high SPF sunscreen. SPF stands for sun protection factor, which is a measure of how well a sunscreen protects our skin against sunburn caused by UVB rays, but not against the long-term damages of UVA radiation.
Moreover, research has shown that high SPFs can be harmful when left on the skin. They are heavily prone to causing rashes and irritation and contain chemicals like oxybenzone which act as hormone disruptors.
Chemical sunscreens are only effective for 2-3 hours after application. They absorb UV rays during this time, but once they stop working, they turn into free radicals which react with DNA cells, increasing the visible signs of ageing and the risk of skin cancer. They actually produce more free radicals within your skin than if you didn’t wear sunscreen at all.
“Scientists do not recommend anything stronger than SPF 15-20 because there is a minimal advantage from the higher SPFs … stronger creams contain greater concentrations of sunscreen agents which themselves can be converted into free radicals by exposure to UV rays,” says Dr Des Fernandes.
Don’t forget that SPF only indicates protection from UVB rays which cause burning, and not UVA rays which cause photoageing, so using a broad-spectrum cream that protects against both is key.

You are better protected using our AVST daily creams by Environ. AVST stands for Advanced Vitamin Skin Therapy. It contains a blend of active ingredients, in particular vitamin A, which increases cellular turnover, and improves the appearance of lines, wrinkles and uneven skin tone. It also helps defend our skin against UV damage.
“The most powerful sun-protective molecule is the retinyl palmitate form of vitamin A, which in adequate doses, can have a photo-protective effect of SPF20 and gives additional protection against UVA,” says Dr Fernandes.
By using a combination of Vitamin A and antioxidants, you can safely expose your skin to the sun for 20 minutes without sunscreen, in order to synthesize vitamin D, which is vital for healthy skin as well as preventing conditions such as osteoporosis, and even cancer.
SAFE IN THE SUNSHINE A-B-C
- Antioxidants are an essential sunscreen ingredient
- Be vigilant – reapply regularly
- Choose to include a daily dose of a vitamin A and antioxidant supplement
